Environmental impact categories
International Life Cycle Data Reference System (ILCD) methodology.
The environmental impact has been selected following the International reference Life Cycle Data system (ILCD) methodology. This protocol was released by the European Commission, Joint Research Centre in 2012. It supports the correct use of the characterization factors for impact assessment as recommended in the ILCD guidance document “Recommendations for Life Cycle Impact Assessment in the European context – based on existing environmental impact assessment models and factors (EC-JRC, 2011)”.
There are 16 environmental impact categories:
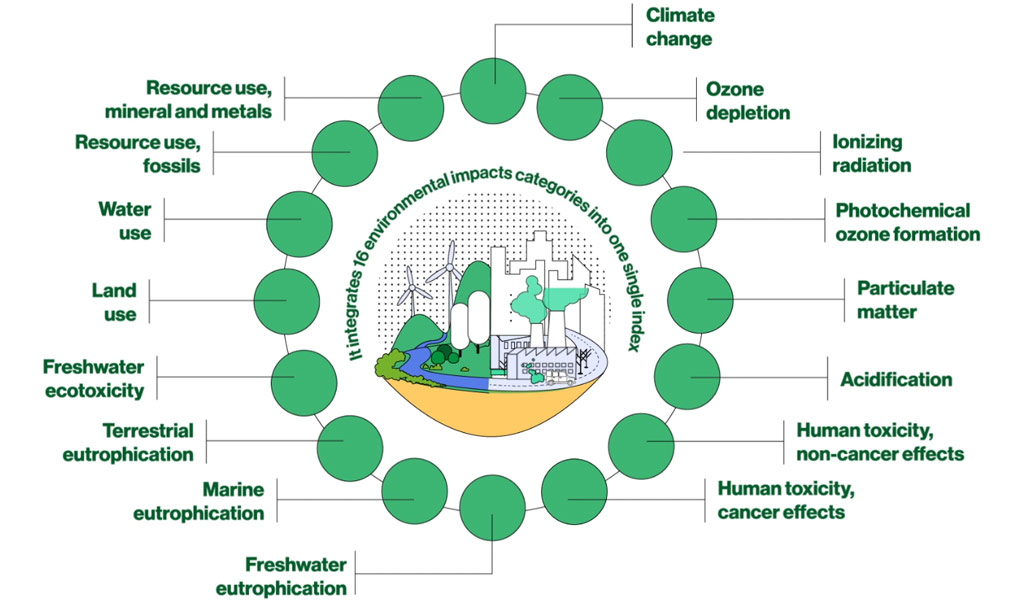
Global Warming Potential calculating the radiative forcing over a time horizon of 100 years.
- Unit: kg CO2 eq
- Reference: IPCC 2013
Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) calculating the destructive effects on the stratospheric ozone layer over a time horizon of 100 years.
- Unit: kg CFC-11 eq
- Reference: World Meteorological Organization (WMO) 1999.
Quantification of the impact of ionizing radiation on the population, in comparison to Uranium 235.
- Unit: kBq U235 eq
- Reference: Frischknecht et al. 2000.
Expression of the potential contribution to photochemical ozone formation. Only for Europe. It includes spatial differentiation
- Unit: kg NMVOC eq
- Reference: Van Zelm et al. 2008.
Quantification of the impact on human health with disease incidence
- Unit: disease incidence
- Reference: Fantke et al. 2016
Comparative Toxic Unit for humans (CTUh) expressing the estimated increase in morbidity in the total human population per unit mass of a chemical emitted (cases per kilogramme). Specific groups of chemicals require further works.
- Unit: CTUh
- Reference: USEtox model, Rosenbaum et al. 2008
Comparative Toxic Unit for humans (CTUh) expressing the estimated increase in morbidity in the total human population per unit mass of a chemical emitted (cases per kilogramme). Specific groups of chemicals require further works. | USEtox model (recommended + interim).
- Unit: CTUh
- Reference: USEtox model, Rosenbaum et al. 2008
Accumulated Exceedance (AE) characterizing the change in critical load exceedance of the sensitive area in terrestrial and main freshwater ecosystems, to which acidifying substances deposit. European-country dependent.
- Unit: molc H+ eq
- Reference: Seppälä et al. 2006 and Posch et al. 2008
Expression of the degree to which the emitted nutrients reach the freshwater end compartment (phosphorus considered as limiting factor in freshwater). European validity. Averaged characterization factors from country dependent characterization factors. | ReCiPe version 1.05.
- Unit: kg P eq
- Reference: ReCiPe version 1.05
Expression of the degree to which the emitted nutrients reach the marine end compartment (nitrogen considered as limiting factor in marine water). European validity. Averaged characterization factors from country dependent characterization factors. | ReCiPe version 1.05.
- Unit: kg N eq
- Reference: ReCiPe version 1.05
Expression of the degree to which the emitted nutrients reach the ecosystem end compartment (nitrogen and phosphorus considered as limiting factors in the terrestrial ecosystem). European-country dependent. | Seppälä et al. 2006 and Posch et al. 2008.
- Unit: mol N eq
- Reference: Seppälä et al. 2006 and Posch et al. 2008
Comparative Toxic Unit for ecosystems (CTUe) expressing an estimate of the potentially affected fraction of species (PAF) integrated over time and volume per unit mass of a chemical emitted (PAF m3 year/kg). Specific groups of chemicals require further works. | USEtox model (recommended + interim).
- Unit: CTUe
- Reference: USEtox model, Rosenbaum et al. 2008
Soil quality index assessing the impacts of land use activities on five soil properties. | Soil quality index based on LANCA (EC-JRC).
- Unit: Pt (Dimensionless)
- Reference: Soil quality index based on LANCA (EC-JRC), Beck et al. 2010 and Bos et al. 2016
User deprivation potential (deprivation-weighted water consumption) Relative Available Water REmaining (AWARE) per area in a watershed, after the demand of humans and aquatic ecosystems has been met. CF are recommended for characterization of blue water consumption only, where consumption is defined as the difference between withdrawal and release of blue water. Therefore, green water, fossil water, sea water and rain water are not to be characterized with this CFs set. The following features of AWARE100 are not included: agricultural/non-agricultural distinction at country level, temporal (monthly) specification, characterization factors at watershed level.
- Unit: m3 depriv
- Reference: Boulay et al. 2016
Abiotic resource depletion fossil fuels (ADP-fossil); based on lower heating value ADP for energy carriers, based on van Oers et al. 2002 as implemented in CML, v. 4.8 (2016). Depletion model based on use-to-availability ratio. Full substitution among fossil energy carriers is assumed.
- Unit: kg Sb eq
- Reference: CML 2002, Guinée et al. 2002 and Van Oers et al. 2002
Abiotic resource depletion (ADP ultimate reserve) for mineral and metal resources, based on van Oers et al. 2002 as implemented in CML, v. 4.8 (2016). Depletion model based on use-to-availability ratio.
- Unit: MJ
- Reference: CML 2002, Guinée et al. 2002 and Van Oers et al. 2002
